
Grotto temples, which are religious niches or caves carved into mountains or rock, were introduced to China along the Silk Road in the 3rd century and, over the course of the following millennium, gradually became a fundamental form of Chinese Buddhist art.
According to a nationwide survey launched by the National Cultural Heritage Administration last year, China has 5,986 cliffside grotto temples and stone carving sites.
In October 2020, the State Council released the country's first national-level guidance focusing on the protection and study of such sites.
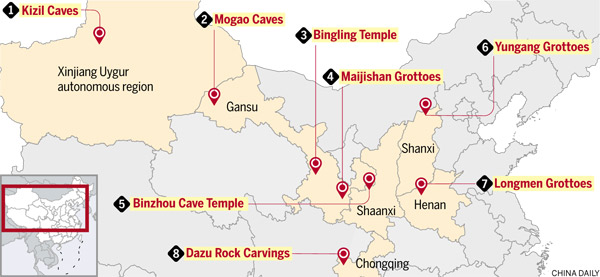
Eight of the most notable examples are included in the UNESCO World Heritage List.

1 Kizil Caves, Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region
These 200-odd caves, with murals from the 3rd to 9th centuries, are believed to compose the earliest-known grotto temple site in China. Many of the relics found there were taken to Europe.
2 Mogao Caves, Gansu province
This complex of 492 extant caves, with their exquisite murals and statues dating from the 4th to 14th centuries, marks a crucial crossroads of the Silk Road. Over 60,000 volumes of manuscripts from its "library cave", now scattered worldwide, are also priceless and encyclopedic recordings predating the Tang Dynasty (618-907).
3 Bingling Temple, Gansu province
This site is home to one of the oldest extant Buddhist grottoes in China, with the time of its creation clearly marked as 420.

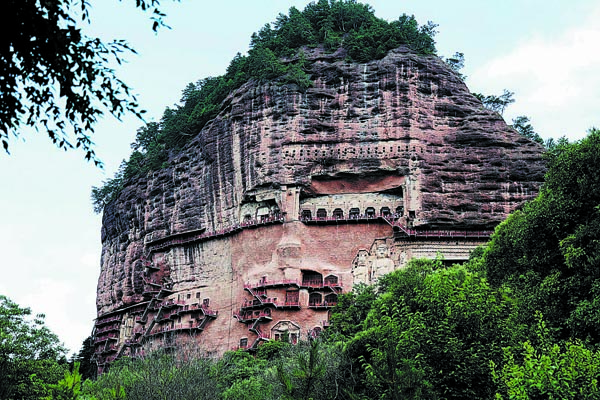
4 Maijishan Grottoes, Gansu province
First carved in the 4th century, the caves are best known for their vividly portrayed, smiling earthen statues, which mix lively visage of people and the solemn countenance of deities.
5 Binzhou Cave Temple, Shaanxi province
Completed in 628, the site displays the crucial transition of grotto temple art into the grand aesthetics of the Tang Dynasty.
6 Yungang Grottoes, Shanxi province
From the 5th century, these 50-odd caves show how grotto art in China was influenced by similar examples in India and evolved into its own style.
7 Longmen Grottoes, Henan province
The 2,000-odd caves dating back to the 5th century are witnesses to the localization of Buddhist art in China, which reached its cultural peak during the Tang Dynasty in the 7th and 8th centuries.
8 Dazu Rock Carvings, Chongqing
Often hailed as "the last monument of grotto temple arts in the world", these carvings, mainly from the 11th to 13th centuries, integrate explanation of Buddhist sutras with folk tales.